- 23 May 2024
- 3 Minutes to read
- Print
- DarkLight
- PDF
PIAM Features
- Updated on 23 May 2024
- 3 Minutes to read
- Print
- DarkLight
- PDF
Feature Overview
Sr. No. | Cross Identity CPIAM Features | Feature Details |
|---|---|---|
Cloud - Privileged Identity Access Management | ||
1. | Single-Sign-On | Cross Identity's Cloud PIAM can be integrated with SAML for Single Sign on to seamless access to servers. |
2. | Advanced Multifactor Authentication | Cross Identity's built-in Multi-Factor Authentication support for selective integrated application access can also be enabled for the CPIAM module. |
3. | Session Manager | Provides granular controls over what privileged users can access and do during a session, as well as the ability to record and audit session activity for compliance purposes. |
4. | Session Recording | All the privileged user sessions, including user activities and changes made to sensitive systems and data, can be recorded in CPIAM. It also provides the ability to replay privileged sessions for forensic analysis and incident response purposes. |
5. | Session Termination | Session Manager in PIAM provides granular control over privileged user sessions, including the ability to terminate sessions (session time out) or revoke access in real time. |
6. | Support for Remote Desktop Protocols and Network Devices | CPIAM solution supports a variety of protocols for connecting servers, including SSH, Telnet, VNC, and RDP. We also support a variety of authentication methods, such as password-based authentication, public key authentication, and two-factor authentication and devices including DB, Router, and any network devices. |
7. | Password Management for PIAM users | The Password Manager in CPIAM stores all privileged account credentials in a secure, centralized vault. This reduces the risk of password theft and unauthorized access to sensitive systems and data. |
Detailed Features
Single Sign on to PIAM Servers
Single Sign to PIAM enables users to access privileged resources through a unified authentication process. CPIAM can be integrated as a SAML application with Cross Identity to perform SSO. This can be configured as SP or IdP-initiated flows.
Advanced Multifactor Authentication
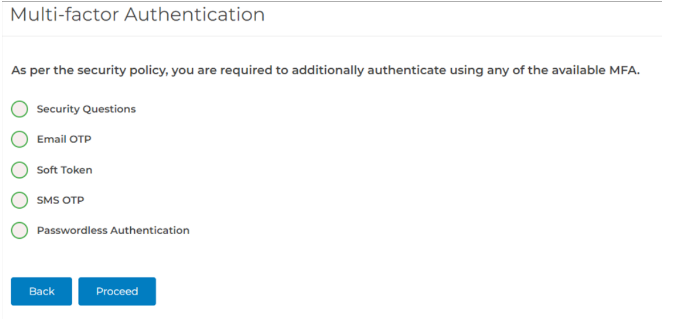
Multifactor Authentication protects your resources with a comprehensive range of user-friendly authentication methods and strengthens security by requiring users to provide additional verification factors.
Cross Identity enables a step-up authentication layer while performing login or Single Sign on to Cloud PIAM (CPIAM). This can be based on various contexts available in the CI solution such as Geolocation, IP Range, Time of access and so on.
The MFA options include:
Security Questions
SMS OTP
Email OTP
Soft Token
Passwordless MFA
Session Manager
Using audits that cannot be altered and important events recorded, CPIAM enables users to maintain compliance. Secure, segregated remote sessions should be established, and all activity should be recorded. End users never make direct connections to the targets, lowering the malware risk of malware.
When any user accesses a particular remote desktop connection, a unique session is created and will appear in the list of active sessions in the session management screen. Each active session is displayed in a sortable table, showing the corresponding user’s username, how long the session has been active, the IP address of the machine from which the user is connecting, and the name of the connection being used.

Session Recording
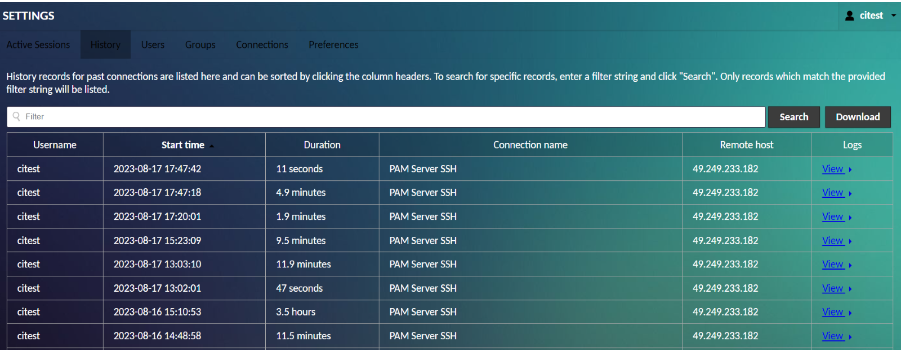
The CIPIAM web application includes support for playing back recordings from the history screen in the administration interface. Still, that support cannot automatically know where those recordings are stored nor how they are named. The extension documented here provides exactly that missing piece, allowing the web application to find recordings on disk so long as they are named appropriately and stored in a specific location.
The availability of a recording is displayed as a “View” link in the “Logs” column of the history table:
Clicking on that link navigates to a screen with a player that loads the recording and allows it to be played back:
Session Termination
The user menu within the CIPIAM menu provides an additional “Disconnect” option that allows you to explicitly close the current connection only. Clicking “Logout” will also implicitly disconnect all active connections, including the current connection.
Support for remote desktop protocols and Network Devices
Our CPIAM solution supports various protocols for connecting servers, including SSH, Telnet, VNC and RDP. We also support a variety of authentication methods, such as password-based authentication, public-key authentication, and two-factor authentication.
This includes support for various remote desktop protocols:
SSH
RDP
VNC
Telnet
Kubernetes
Our CPIAM solution supports many devices, including databases, routers and network devices such as DB/ Routers and Network Devices.
CPIAM solution provides centralized control and monitoring of privileged access to databases. This includes database management systems like Oracle, Microsoft SQL Server, MySQL, PostgreSQL, and more. PIAM solutions also extend their coverage to routers, switches, firewalls, and other network infrastructure components. This is essential to maintaining control over network configurations and minimizing the risk of unauthorized changes.
Password Management for PIAM users
Privileged credential management refers to the vaulting and secure storage of privileged credentials and secrets. A password policy establishes specific rules, best practices and tools that can help your organization manage user credentials efficiently and securely. The password manager in CPIAM stores all privileged account credentials in a secure, centralized vault reducing the risk of password theft and unauthorized access to sensitive systems and data.
It also enforces strong password policies to ensure that all the passwords meet minimum complexity requirements, such as length, complexity, and expiration.
.png)







.png)